Abstract
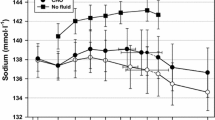
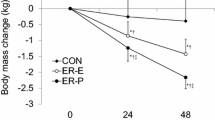
In this study, we examined whether athletes, who typically replace only ≈50% of their fluid losses during moderate-duration endurance exercise, should attempt to replace their Na+ losses to maintain extracellular fluid volume. Six male cyclists performed three 90-min rides at 65% of peak O2 uptake in a 32°C environment and ingested either no fluid (NF), 1.2 l of water (W), or saline (S) containing 100 mmol of NaCl · l−1 to replace their electrolyte losses. Both W and S conditions decreased final heart rates by ≈10 betas · min−1 (P < 0.005) and reduced falls in plasma volume (PV) by ≈4% (P < 0.05). Maintenance of PV after 10 min in the W trial prevented further rises in plasma concentrations of Na+ [Na+], Cl− and protein but in the S and NF trials, plasma [Na+] continued to increase by ≈4 mEq · l−1. Differences in plasma [Na+] had little effect on the ≈2.4 l fluid, ≈120 mEq Na+ and ≈50 mEq K+ losses in sweat and urine in the three trials. The main effects of W and S were on body fluid shifts. During the NF trial, PV and interstitial fluid (ISF) and intracellular fluid (ICF) volumes decreased by ≈0.1, 1.2 and 1.0 l, respectively. In the W trial, the ≈1.2 l fluid and ≈120 mEq Na+ losses contracted the ISF volume, and in the S trial, ISF volume was maintained by the movement of water from the ICF. Since the W and S trials were equally effective in maintaining PV, Na+ ingestion may not be of much advantage to athletes who typically replace only ≈50% of their fluid losses during competitive endurance exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 13 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanders, B., Noakes, T. & Dennis, S. Water and electrolyte shifts with partial fluid replacement during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 80, 318–323 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050598
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050598